Higher gas prices mean switch to coal, EIA finds
18 October 2021
Use of coal for power gen in U.S. expected to rise 22% this year
Driven in part by higher natural gas prices, coal-fired power generation in the U.S. is expected to rise 22% in 2021, according to the U.S. Energy Information Agency’s (EIA) latest estimate.
The EIA’s latest Short-Term Energy Outlook estimates that 2021 will mark the first year-over-year increase in coal generation since 2014.
“Coal and natural gas have been the two largest sources of electricity generation in the United States,” the report states. “In many areas of the country, these two fuels compete to supply electricity based on their relative costs. U.S. natural gas prices have been more volatile than coal prices, so the cost of natural gas often determines the relative share of generation provided by natural gas and coal.”
Because natural gas-fired power plants are generally more efficient than coal-fired plants, natural gas-fired generation tend to have an economic advantage even if natural gas prices are slightly higher than coal prices. Between 2015 and 2020, the cost of natural gas delivered to electric generators remained relatively low and stable.
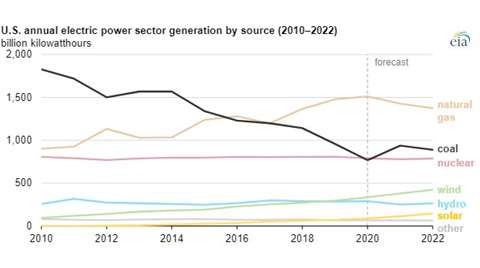
According to the EIA, this year’s natural gas prices have been much higher than in recent years. The year-to-date delivered cost of natural gas to U.S. power plants has averaged US$4.93 per million British thermal units (Btu), more than double last year’s price.
“The overall decline in U.S. electricity demand in 2020 and record-low natural gas prices led coal plants to significantly reduce the percentage of time that they generated power,” the report states. “In 2020, the utilization rate (known as the capacity factor) of U.S. coal-fired generators averaged 40%. Before 2010, coal capacity factors routinely averaged 70% or more. This year’s higher natural gas prices have increased the average coal capacity factor to about 51%, which is almost the 2018 average.”
Although rising natural gas prices have resulted in more U.S. coal-fired generation than last year, this increase in coal generation will most likely not continue, according to the report. The electric power sector has retired about 30% of its generating capacity at coal plants since 2010, and no new coal-fired capacity has come online in the United States since 2013. In addition, coal stocks at U.S. power plants are relatively low, and production at operating coal mines has not been increasing as rapidly as the recent increase in coal demand.
“For 2022, we forecast that U.S. coal-fired generation will decline about 5% in response to continuing retirements of generating capacity at coal power plants and slightly lower natural gas prices,” the report states.